Basic Hospital and Medical Supplies Essential for Health Organizations
Proper equipment in clinics and other care facilities, as well as its proper usage, is fundamental for saving people’s lives. Medical professionals, such as doctors, can analyse and take care of a patient’s medical needs thanks to the usage of equipment. As a result, it is critical to understand the various types of medical equipment available and how they all work cohesively together to support and treat the patient appropriately.
Every day, the number of different types of health care supplies grows, which is why they’re classified into several categories. Hospital and post-surgery care constantly evolve, so be certain that your physician’s office, DME, lab, long-term care facility, or post-acute care setting has the skills and resources necessary for successful outcomes.

1. Transport and Storage
Medical supply storage and transportation equipment. This equipment is used to transport a variety of supplies to patients and medical personnel for a variety of purposes. The following are the most frequent types of storage and transportation as essential parts of hospital equipment:
Case Cart
A case cart can be defined simply as a specially prepared cart. Contains all of the supplies needed by the surgical team to perform a complete procedure on a specific patient, as well as the aseptic technique.
Storage Cart
A storage cart is an integral part of medical supplies since it can also be used to store prohibited substances, which might get your hospital into problems if they fall into the wrong hands.
Utility Cart
A mobile medical utility cart gives your team fast access to medical records from anywhere in the workplace.
Custom Surgical (Procedure) Tray
A CPT, or custom procedure tray, is a collection of hospital equipment designed to supply disposable things required during surgery. They are often developed and configured for your specific procedure requirements. A unique procedure tray’s contents are packed together and delivered in a single sterile pack. Surgical blades, stitches, lesion dressing, cardiac catheters, surgical wipes, implants, and surgical drapes are the most common items in the CPT.
Instrument Trolley
An instrument trolley, also known as a medicine trolley, is primarily used in hospitals and medical centres to transport medications and surgical tools. These trolleys are usually square metal trolleys with rollers on each leg to let the trolley move around quickly.
2. Durable Medical Equipment
DME is a sort of medical equipment that is intended to be long-lasting and to give patients safe and comfortable assistance. This type of equipment is mostly utilised for therapeutic purposes and can be used in both the hospital and at home. The majority of long-lasting medical equipment is built with load-bearing strength and non-slip features. Common Durable Medical Equipment (DME) include:
- Wheelchairs
- Mobility assistive equipment – walkers, canes, crutches
- Hospital beds
- Ventilators
- Lifts
- Traction Equipment
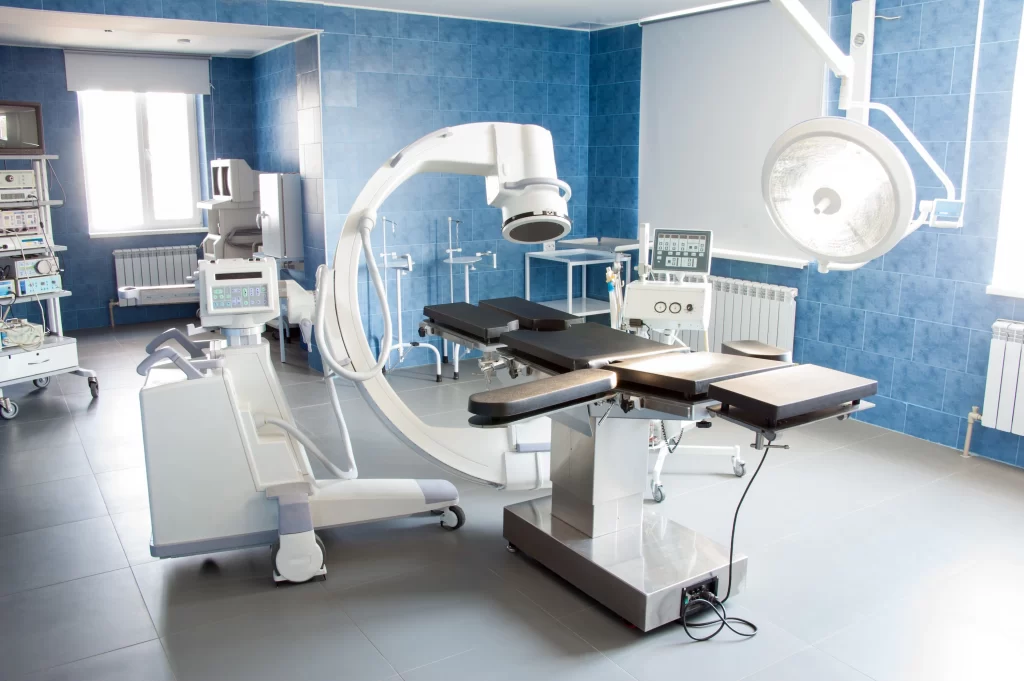
3. Diagnostic Medical Equipment
As you can guess, this type of equipment or supplies are used to diagnose, test, or locate a patient’s condition, and to discover any abnormalities in the organs or other regions of the body that may be causing the symptoms. Medical practitioners would be unable to accurately diagnose and treat patients without diagnostic equipment.
Common diagnostic equipment used in hospitals and clinics is imaging machines such as X-Rays, MRI scans, CT scans, as well as medical instruments like stethoscopes and thermometers.
4. Electronic Medical Devices
Electronic equipment is used to create, monitor, and record bodily activities like heartbeats and brain waves. Electronic medical supplies come in a variety of types, including:
- Electronic Medical Records
- Medical Imaging Software
- Heart Rate Monitors
- Blood Pressure Monitors
- Ultrasound
- Medication Pumps
- Mobile Technology Carts
- Mobile Workstations
- Computers on Wheels
- Powered Medical Equipment
- Pacemakers
- Defibrillators
5. Medical Surgical Equipment
The accuracy of surgical equipment and instruments is critical to the outcome of a surgery. There are numerous sorts of surgical equipment, each with its particular function. The most common surgical equipment and instruments include:
- Surgical Tables
- Utility Tables
- Instrument Tables
- Hampers
- Mayo Stands
- Solution Stands
- Kickbuckets
- Surgical Table Pads
- Leg and Arm Supports
6. Acute (Post Surgery) Care
This type of equipment and supplies are used daily for patient care and must be handled by a medical professional. This includes:
- Trays for general use
- Trays for minor procedures
- Kits for wound care and skincare
- Monitoring devices
- Non-surgical equipment
7. Procedural Medical Equipment
Procedural medical equipment is used in a variety of medical operations and contains a variety of various items. It is used to aid and facilitate operations, so the following items are a must:
- Surgical clamps
- Scalpels
- Forceps
- Gloves
- Operating Scissors
- Headlights
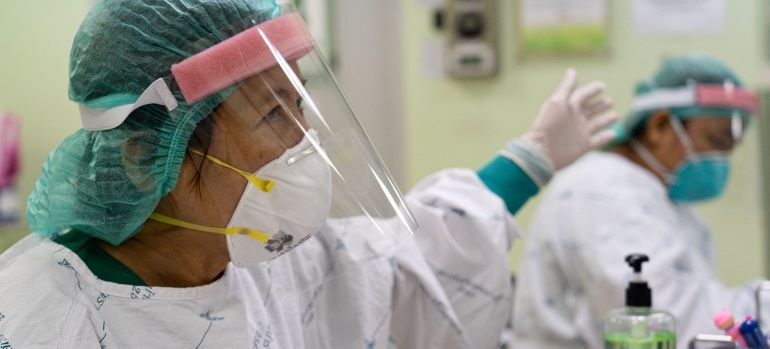
8. Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment is carefully chosen to ensure compatibility with the chemicals, environment and the process taking place.
Eye Protection
Safety glasses or chemical goggles must be worn before entering any wet bench lab, including cell culture facilities. This includes lab visitors, GT maintenance and custodial workers, as well as staff and students. Chemical goggles may be required for specific processes where safety glasses are regarded as insufficient.
Lab Coats
There are different types and styles of lab coats designed to protect staff and keep things hygienic.
Traditional Lab Coat
It’s usually a poly/cotton blend, with one-piece, lined, notched lapel collar with front closures.
Barrier Lab Coat
Designed with knit cuffs to prevent exposure to blood-borne pathogens and other potentially infectious materials.
Flame Resistant Lab Coat
Designed for protection when working with flammable chemicals, they’re available as Nomex (i.e. synthetic fibre) or treated cotton, and unlike regular cotton they provide the needed safety even after repeated washes.
Chemically Resistant Gloves
Gloves, in particular, must be carefully chosen: they must be chemically resistant while also not putting the wearer at risk due to loss of dexterity, or risk of ergonomic injury (such as increased muscle strain from gloves that are too heavy or stiff for pipetting, handling small objects, etc.). They also shouldn’t increase the risk of being caught in rotating equipment from gloves that are too loose on the user’s hands.

