Explaining the Two Basic Types of Solar Charge Controllers
A solar charge controller is a device which helps control the current or voltage that goes through the solar system. This feature is incredibly important in solar systems as it helps prevent the batteries from overcharging. Generally, a 12V panel is capable of putting out 16V to 20V. However, most solar batteries require 14V or 15V to be completely charged. With that said, a 12V solar system can greatly benefit from a charge controller and preserve the longevity of your solar batteries.
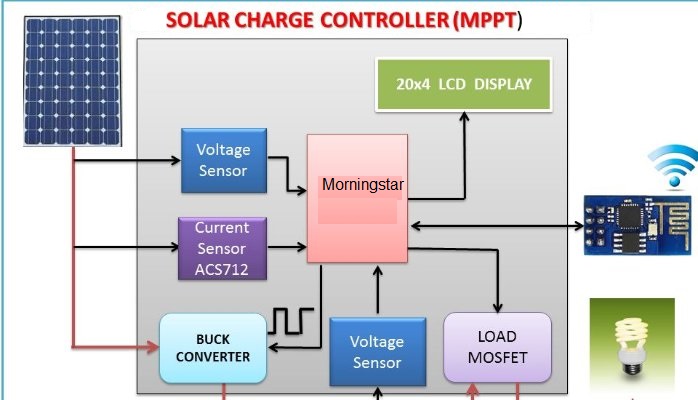
When looking for solar charge controllers for sale, you’ll come accross two basic types – MPPT (maximum power point tracking) and PWM ( pulse-width modulation) controllers. There are significant differences between the two, so you have to consider that before you decide on which solar charge controllers for sale are better suited for you.
For starters, PWM is incredibly durable, can be used for many years and it is built on time tested technology. Moreover, it’s the more affordable option and it’s available in multiple sizes up to 60 amps. However, the regulation of PWM controllers is more difficult to control because the controller has to match the battery bank. MPPT controllers on the other hand, have a better charging efficiency, and they’re available in sizes up to 80 amps. However, given the fact that they’re larger in size and capacity, they’re also more expensive. On the bright side, they easily convert for batteries and keep a higher input voltage.
MPPT controllers utilize an electronic method which captures the majority of the powers from the cell and panels. MPPT controllers are considered the more advanced and sophisticated version of PWM controllers because they can determine the right amount the batteries need, and can absorb more voltage. Additionally, they raise the output current and transform the module operation voltage into the battery’s voltage at the same time. The controller provides filtering, current conversion and regulation for driving different loads, such as power grids, motors, and batteries by incorporating an electric power converter.
PMW controllers, on the other hand, operate by adjusting the charging rates depending on how full the battery is, and are more complicated to adjust to the ideal levels. However, they make the 3 stage process extremely efficient by making use of high-frequency electric pulses to consistently shift the amps that are delivered by properly adjusting the length of the pulses. PMW controllers are typically used for 12V batteries which emit around 30A. They measure the output and regulate the voltage, and in cases when the voltage is lower than needed – the switch is turned on. When it’s above the needed level – the switch is turned off.